
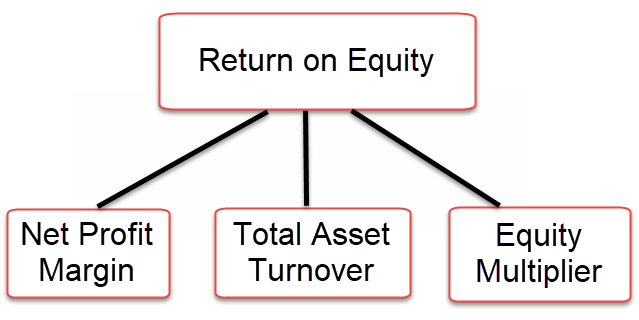
The DuPont formula, also known as the strategic profit model, is a common way to decompose ROE into three important components. Since much financial manipulation is accomplished with new share issues and buyback, the investor may have a different recalculated value 'per share' (earnings per share/book value per share).įurther information: DuPont analysis § ROE analysis, and Financial risk management § Corporate finance ROE is calculated from the company perspective, on the company as a whole.If the shares are bought at a multiple of book value (a factor of x times book value), the incremental earnings returns will be reduced by that same factor (ROE/ x). The growth rate will be lower if earnings are used to buy back shares.If the dividend payout is 20%, the growth expected will be only 80% of the ROE rate. The sustainable growth model shows that when firms pay dividends, earnings growth lowers.While higher ROE ought intuitively to imply higher stock prices, in reality, predicting the stock value of a company based on its ROE is dependent on too many other factors to be of use by itself. ROE is also a factor in stock valuation, in association with other financial ratios. ROEs of 15–20% are generally considered good. As with return on capital, a ROE is a measure of management's ability to generate income from the equity available to it. ROE is especially used for comparing the performance of companies in the same industry. ROE is equal to a fiscal year net income (after preferred stock dividends, before common stock dividends), divided by total equity (excluding preferred shares), expressed as a percentage. The formula ROE = Net Income / Average Shareholders' Equity ROE is a metric of how well the company utilizes its equity to generate profits. ROE measures how many dollars of profit are generated for each dollar of shareholder's equity. Because shareholder's equity can be calculated by taking all assets and subtracting all liabilities, ROE can also be thought of as a return on assets minus liabilities. The return on equity ( ROE) is a measure of the profitability of a business in relation to the equity. If the company retains these profits, the common shareholders will only realize this gain by having an appreciated stock.Measure of the profitability of a business This could indicate that Tammy’s is a growing company.Īn average of 5 to 10 years of ROE ratios will give investors a better picture of the growth of this company.Ĭompany growth or a higher ROE doesn’t necessarily get passed onto the investors however. Tammy’s ratio is most likely considered high for her industry. In other words, shareholders saw a 180 percent return on their investment. This means that every dollar of common shareholder’s equity earned about $1.80 this year.
Tammy would calculate her return on common equity like this:Īs you can see, after preferred dividends are removed from net income Tammy’s ROE is 1.8. Tammy also had 10,000, $5 par common shares outstanding during the year. Tammy reported net income of $100,000 and issued preferred dividends of $10,000 during the year. Tammy’s Tool Company is a retail store that sells tools to construction companies across the country. This helps track a company’s progress and ability to maintain a positive earnings trend. Many investors also choose to calculate the return on equity at the beginning of a period and the end of a period to see the change in return. Since every industry has different levels of investors and income, ROE can’t be used to compare companies outside of their industries very effectively. Higher ratios are almost always better than lower ratios, but have to be compared to other companies’ ratios in the industry. That being said, investors want to see a high return on equity ratio because this indicates that the company is using its investors’ funds effectively. In other words, this ratio calculates how much money is made based on the investors’ investment in the company, not the company’s investment in assets or something else.

Unlike other return on investment ratios, ROE is a profitability ratio from the investor’s point of view-not the company. Return on equity measures how efficiently a firm can use the money from shareholders to generate profits and grow the company. Preferred dividends are then taken out of net income for the calculation.Īlso, average common stockholder’s equity is usually used, so an average of beginning and ending equity is calculated.

In this case, preferred dividends are not included in the calculation because these profits are not available to common stockholders. Most of the time, ROE is computed for common shareholders.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
